

Joining time-scaled patches to backbones results in species-level trees of extant Mammalia with all branches estimated under the same modeling framework, thereby facilitating rate comparisons among lineages as disparate as marsupials and placentals.
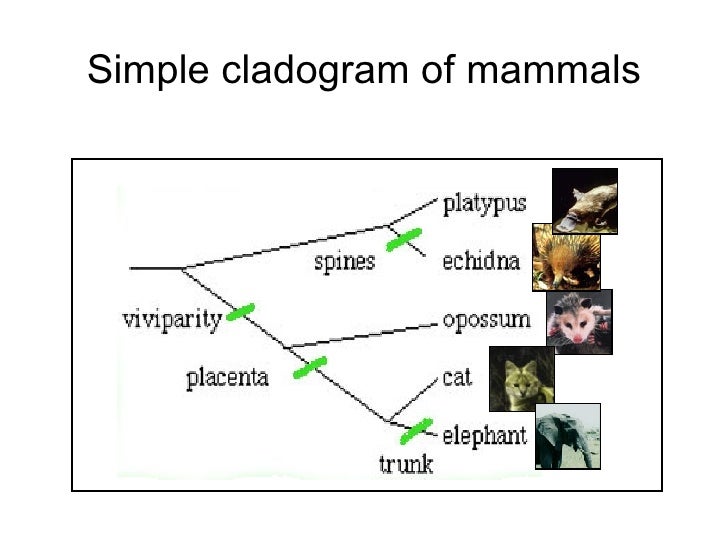
Species unsampled for DNA are either excluded (“DNA-only” trees) or imputed within taxonomic constraints using branch lengths drawn from local birth–death models (“completed” trees). Our “backbone-and-patch” approach to tree building applies a newly assembled 31-gene supermatrix to two levels of Bayesian inference: (1) backbone relationships and ages among major lineages, using fossil node or tip dating, and (2) species-level “patch” phylogenies with nonoverlapping in-groups that each correspond to one representative lineage in the backbone. To establish a robust evolutionary timescale for all approximately 6,000 living species of mammals, we developed credible sets of trees that capture root-to-tip uncertainty in topology and divergence times. Yet inferring reliable phylogenetic trees for thousands of species involves numerous trade-offs that have limited their utility to comparative biologists. Big, time-scaled phylogenies are fundamental to connecting evolutionary processes to modern biodiversity patterns.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
